Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (20): 3730-3737.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.20.017
Previous Articles Next Articles
Ruanmai preparation prevents vascular calcification in mice
Situ Yong-li, Xie Ai-mei, Zheng Zhi-ming, Lu Han-yun, Wu Tie
- Department of Pharmacology, Pharmacy College, Guangdong Medical College, Zhanjiang 524023, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2012-10-18Revised:2012-12-06Online:2013-05-14Published:2013-05-14 -
Contact:Wu Tie, Master, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Pharmacology, Pharmacy College, Guangdong Medical College, Zhanjiang 524023, Guangdong Province, China wutie2@163.com -
About author:Situ Yong-li★, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Pharmacology, Pharmacy College, Guangdong Medical College, Zhanjiang 524023, Guangdong Province, China 562004233@qq.com -
Supported by:Science and Technology Plan Projects of Guangdong Province, No. 2010B06050
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Situ Yong-li, Xie Ai-mei, Zheng Zhi-ming, Lu Han-yun, Wu Tie. Ruanmai preparation prevents vascular calcification in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(20): 3730-3737.
share this article

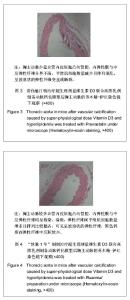
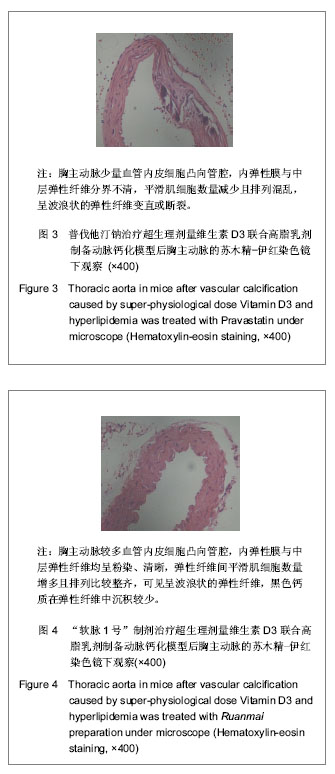
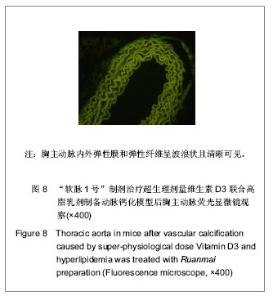
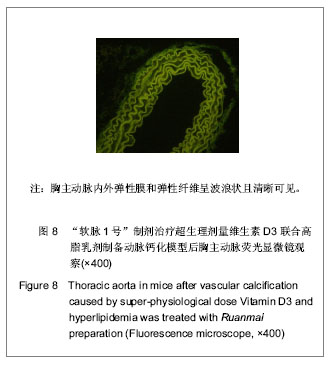
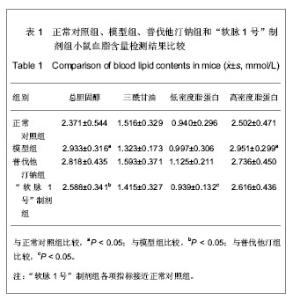
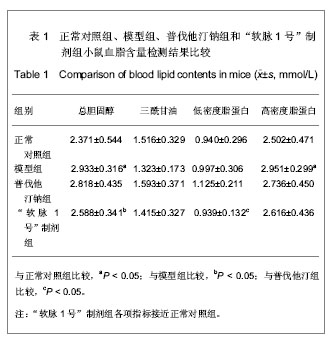
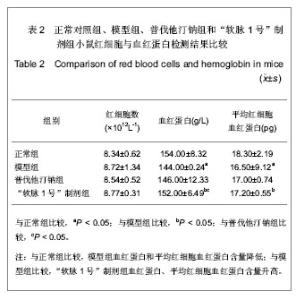
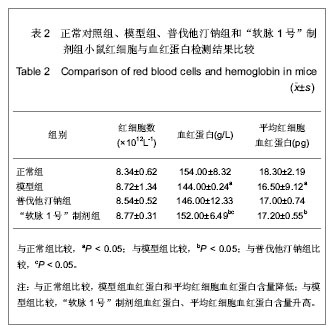
2.1 实验动物数量分析 纳入动物数量40只,分4组进行实验,其中普伐他汀钠组有1只、维生素D3+高脂乳剂模型组有1只小鼠因维生素D3急性中毒而死,其余小鼠存活至实验结束,进入结果分析38只。 2.2 胸主动脉大体观察与组织学观察 胸主动脉的大体观察:正常对照组胸主动脉血管外壁光滑,呈淡粉色半透明状,柔软而富有弹性,触之光滑无沙粒感,管壁厚度均匀。模型组胸主动脉血管外壁凹凸不平,团块状灰白色突起弥漫性分布,管壁僵硬易断,触之有沙粒感,管壁厚薄不均。普伐他汀钠组胸主动脉血管外壁凹凸不平,团块状灰白色突起弥漫性分布,有沙粒感,管壁厚薄不均。“软脉1号”制剂组比模型组有所改善,胸主动脉血管外壁凹凸不平减轻,团块状灰白色突起弥漫性分布减少,有沙粒感,管壁厚薄比较均匀。 胸主动脉的镜下观察:正常对照组观察可见胸主动脉血管壁结构清晰,血管内中外膜分界清楚,内皮细胞完整、突向管腔排布,内弹性膜与中层弹性纤维均呈粉染、清晰,波浪状走向,弹性纤维间平滑肌细胞呈梭形,排列整齐而均匀,管壁无黑色钙质沉积,内外弹性膜结构完整,见图1。 模型组观察可见胸主动脉血管内皮细胞消失,有大量黑色钙质沉积于中层弹性纤维中,管壁弹性纤维间距扩大,弹性纤维结构模糊、分辨不清,走向变直,部分断裂,平滑肌细胞坏死消失,内外弹性膜结构不完整,见图2。"

| [1] Bao J, Chen XX, Shen CX. Zhonghua Linchuang Yishi Zazhi. 2010;4(3):318-321.鲍骏,陈肖霞,沈成兴.冠状动脉钙化危险因素研究进展[J].中华临床医师杂志,2010, 4(3):318-321. [2] Takasu J, Katz R, Shavelle DM, et al. Inflammation and descending thoracic aortic calcification as detected by computed tomography: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 2008;199(1):201-206.[3] Yao LF. Tianjin Yaoxue. 2010;22(2):72-74.姚立枫.他汀类药物安全性研究进展[J].天津药学,2010,22(2): 72-74.[4] Houslay ES, Cowell SJ, Prescott RJ, et al. Progressive coronary calcification despite intensive lipid-lowering treatment: a randomised controlled trial. Heart. 2006;92(9): 1207-1212.[5] Terry JG, Carr JJ, Kouba EO, et al. Effect of simvastatin (80 mg) on coronary and abdominal aortic arterial calcium (from the coronary artery calcification treatment with zocor [CATZ] study). Am J Cardiol. 2007;99(12):1714-1747.[6] Zhao YW, Yang X, Dong CJ, et al. Wujing Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2009;8(3):260-262.赵艳威,杨宣,董璨瑾,等.丹参素及原儿茶醛研究进展[J]. 武警医学院学报,2009, 8(3):260-262.[7] Zhou XD, Dong XF, Tong JM. Dongwu Yingxiang Xuebao. 2010; 22(4):817-822.周筱丹,董晓芳,佟建明.维生素E的生物学功能和安全性评价研究进展[J].动物营养学报,2010,22(4):817-822. [8] Zhou CY, Zhang X, Cai CY, et al. Chuanbei Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2003;18(2):1-3.周春阳,张翔,蔡春燕,等.硒和维生素E对实验性高脂血症大鼠血脂及肝肾功能的影响[J].川北医学院学报,2003,18(2):1-3.[9] Chen HM, Gao NN, Yang RM, et al. Zhongguo Shiyan Dongwu Xuebao. 2010;18(3):199-203.陈慧敏,高南南,杨润梅,等.高脂饮食豚鼠高密度脂蛋白代谢的特点[J].中国实验动物学报,2010,18(3):199-203.[10] Kang HX, Wu T. Shizhen Guoyi Guoyao. 2010;21(6): 1522-1524.康海仙,吴铁.动物油和维生素D3诱导小鼠动脉钙化研究[J].时珍国医国药,2010,21(6):1522-1524.[11] Parhami F, Morrow AD, Balucan J, et a1.Lipid Oxidation Products Have Opposite Effects on Calcifying Vascular Cell and Bone Cell Differentiation:A Possible Explanation for the Paradox of Arterial Calcification in Osteoporotic Patients.Arterioscler Thmmb Vasc Biol. 1997;17(4):680-687. [12] Hung CR, Chen WH, Wang PS. Protective effect of lysozyme chloride on gastric oxidative stress and hemorrhagic ulcers in severe atherosclerotic rats. Med Sci Monit. 2007;13(12): BR271- 279.[13] Wu Y, Li J, Wang J, et al. Anti-atherogenic effects of centipede acidic protein in rats fed an atherogenic diet. J Ethnopharmacol. 2009;122(3):509-516.[14] Hsu JJ, Tintut Y, Demer LL. Vitamin D and osteogenic differentiation in the artery wall. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008; 3(5):1542-1547.[15] Cardús A, Parisi E, Gallego C, et al. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 stimulates vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation through a VEGF-mediated pathway. Kidney Int. 2006;69(8): 1377-1384.[16] Kang HX, Wu , Cui L. Zhongguo Dongmaihua Zazhi. 2009;17(4): 294-296.康海仙,吴铁,崔燎.超生理剂量维生素D3致小鼠动脉硬化及机制[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2009, 17(4):294-296.[17] Grases F, Sanchis P, Perello J, et al. Effect of crystallization inhibitors on vascular calcifications induced by vitamin D: a pilot study in Sprague-Dawley rats.Circ J. 2007;71(7): 152-156.[18] Be?towski J, Atanassova P, Chaldakov GN, et al. Opposite effects of pravastatin and atorvastatin on insulin sensitivity in the rat: role of vitamin D metabolites. Atherosclerosis. 2011; 219(2): 526-531.[19] Backes JM, Howard PA. Association of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors with neuropathy.ANN Pharmacother. 2003;37(2): 274-278.[20] Shen LH, Wang BY, Wang CQ, et al. Zhongguo Zhongyi Jizheng. 2004;13(11):764-765.沈玲红,王彬尧,王长谦,等.原儿茶醛对人红细胞胞浆游离钙浓度的影响[J]. 中国中医急症,2004,13(11):764-765. [21] Shen LH, Wang BY, Wang CQ, et al. Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi. 2004;29(10):984-988.沈玲红,王彬尧,王长谦,等.丹参注射液及其活性成分丹参素、原儿茶醛对人红细胞胞浆Ca2+浓度影响的实验研究[J].中国中药杂志,2004,29(10):984-988.[22] Han CJ, Lin R, Liu JT, et al. Zhongyaocail. 2007;30(12):1541- 1544.韩纯洁,林蓉,刘俊田,等.原儿茶醛对OX-LDL损伤的血管内皮细胞保护作用[J].中药材,2007,30(12):1541-1544. [23] Xu ZP, Zhang BL, Li SZ, et al. Tianjin Zhongyi. 2002;19(1): 49-50.徐宗佩,张伯礼,李尚珠,等.中药单体原儿茶醛对瘀血证患者单核细胞趋化游走能力的影响[J].天津中医,2002,19(1):49-50.[24] Xu JS, Shen J, Cheng YY, et al. Simultaneous detection of seven phenolic acids in Danshen injection using HPLC with ultraviolet detector.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2008;9(9): 728-733.[25] Kim KJ, Kim MA, Jung JH. Antitumor and antioxidant activity of protocatechualdehyde produced from Streptomyces lincolnensis M-20. Arch Pharm Res. 2008;31(12):1572-1577.[26] Yukiko K, Nakamura, Stanley T. Omaye. Vitamin E-modulated gene expression associated with ROS generation. Journal of Functional Foods. 2009,1(3):241-252.[27] Theriault A, Chao JT, Gapor A. Tocotrienol is the most effective vitamin E for reducing endothelial expression of adhesion molecules and adhesion to monocytes. Atherosclerosis. 2002;160(1):21-30.[28] Ashfaq MK, Zuberi HS, Anwar Waqar M. Vitamin E and beta-carotene affect natural killer cell function. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2000;51 Suppl:S13-20.[29] Wu GP, Zhang RX. Guoji Mianyixue Zazhi. 2008;31(2): 105-109.吴革平,章如新.三种脂溶性维生素的免疫调节作用及其研究进展[J].国际免疫学杂志,2008, 31(2):105-109. [30] Parker RA, Pearce BC, Clark RW, et al. trienols regulate cholesterol production in mammalian cells by post-transcriptional suppression of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. J Biol Chem. 1993;268(15):11230-11238.[31] Pearce BC, Parker RA, Deason ME, et al. Hypocholesterolemic activity of synthetic and natural tocotrienols. J Med Chem. 1992;35(20):3595-3606.[32] Chao JT, Gapor A, Theriault A. Inhibitory effect of delta-tocotrienol, a HMG CoA reductase inhibitor, on monocyte-endothelial cell adhesion. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2002;48(5):332-337.[33] Pearce BC, Parker RA, Deason ME, et al. Inhibitors of cholesterol biosynthesis. 2. Hypocholesterolemic and antioxidant activities of benzopyran and tetrahydronaphthalene analogues of the tocotrienols. J Med Chem. 1994;37(4):526-541. |
| [1] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [2] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [3] | Zhao Zhongyi, Li Yongzhen, Chen Feng, Ji Aiyu. Comparison of total knee arthroplasty and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treatment of traumatic osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 854-859. |
| [4] | Liu Yang, Gong Yi, Fan Wei. Anti-hepatoma activity of targeted Pluronic F127/formononetin nanocomposite system in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 526-531. |
| [5] | Chen Siyu, Li Yannan, Xie Liying, Liu Siqi, Fan Yurong, Fang Changxing, Zhang Xin, Quan Jiayu, Zuo Lin. Thermosensitive chitosan-collagen composite hydrogel loaded with basic fibroblast growth factor retards ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2472-2478. |
| [6] | Chen Zhenyu, Zhang Xiaoning, Luo Yuxin, Liang Jianwei, Yan Chi. Evaluation of silk fibroin/curcumin composite film for promoting wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2554-2561. |
| [7] | Wang Donghui, Wu Xin, Sun Ningning, Zhang Han, Gao Jianfeng. Electroacupuncture intervention on the expression of synaptic plasticity-related proteins in the hippocampi of mice with radiation-induced brain injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2205-2210. |
| [8] | Zhang Jingying, Sun Xiaolin, Geng Lixia. Therapeutic mechanism of adipose mesenchymal stem cells in mice with systemic sclerosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2011-2017. |
| [9] | Wang Liqun, Li Yuxi, Jin Rongjiang, Wang Wenchun, Pang Richao, Zhang Anren. Application of functional near-infrared spectroscopy in the study of depression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1799-1804. |
| [10] | Hua Hong, Xie Tongling, Hao Guiliang. Immunomodulatory effect of human adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells on skin transplantation between different mouse strains [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 73-77. |
| [11] | Xu Guofeng, Li Xuebin, Tang Yifan, Zhao Yin, Zhou Shengyuan, Chen Xiongsheng, Jia Lianshun. The role of autophagy in ossification of the human ligamentum flavum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1174-1181. |
| [12] | Wan Huazhe, Chai Guangxin, Xiao Xiaoling, Huang Wenying. Effects of phellinus igniarius crude polysaccharides on sporting ability and free radical metabolism of skeletal muscle in mice suffering passive smoking [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 689-693. |
| [13] | Cheng Xue, Fang Hong, Zhang Yunke, Wu Yingen. Interventional mechanism of Feibi prescription on extracellular matrix transformation in a mouse model of pulmonary fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 5038-5043. |
| [14] |
Wen Shuangwei, Wu Qingmei.
Aerobic exercise combined with levothyroxine and vitamin D3 relieves osteoporosis in subclinical hypothyroidism rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4118-4124. |
| [15] |
Hou Xiaolin, Liang Jun, Yang Cheng, Cui Meihua.
Co-transplantation of adipose mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells in ulcerative colitis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 3981-3987. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||